Jammu And Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the largest producer of apples, walnuts, and cherries in India. It is also the largest producer of saffron, one of the most expensive spices in the world.
Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) is a Union Territory (UT) of India, located in the country’s northern part, adventure, pilgrimage, spiritual, and health tourism.
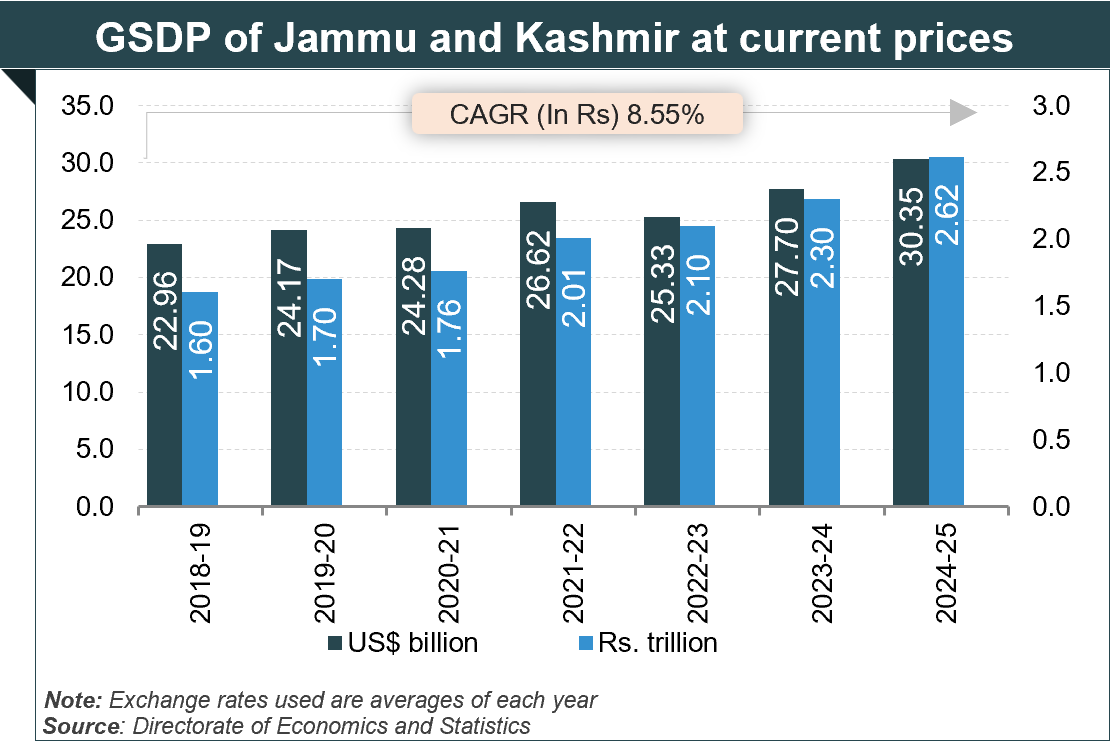
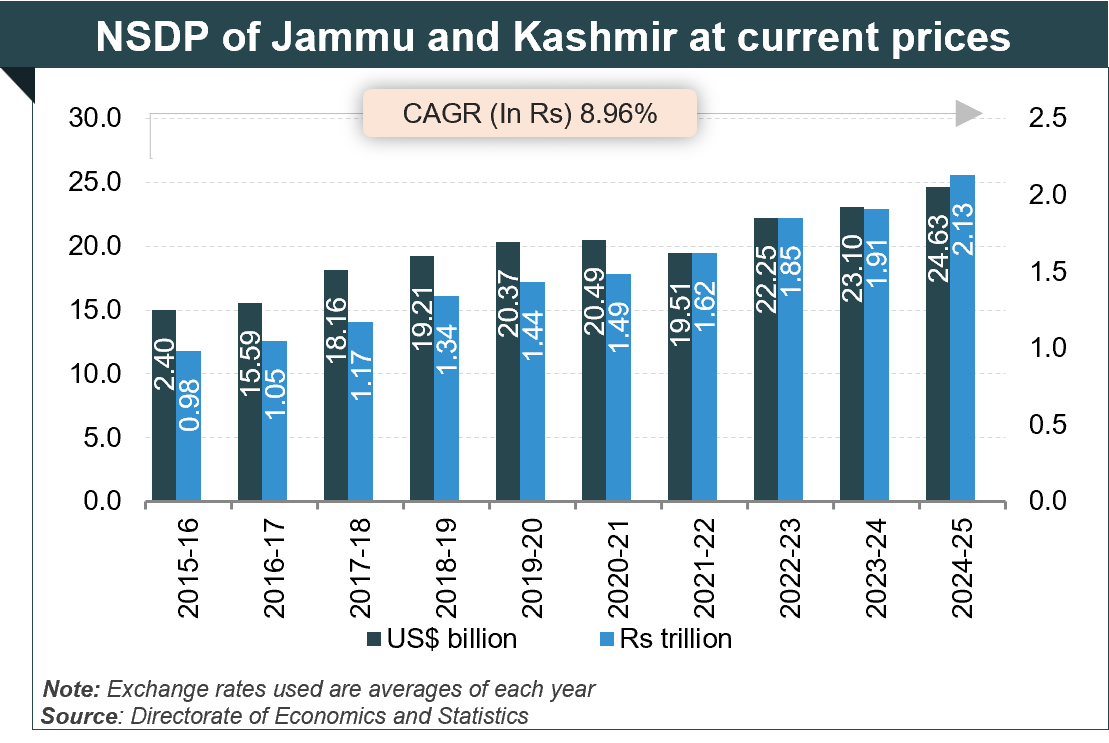
The economy is primarily services based and agri-oriented at current prices, J&K’s Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) was Rs. 2.62 trillion (US$ 30.35 billion) in 2024-25. The UT’s GSDP increased at a CAGR of 8.55 % between 2018-19 and 2024-25.
A vast natural resource base has enabled J&K to develop land for cultivating major fruits. With varied agro-climatic conditions, the scope for horticulture is significantly high in J&K. Food processing and an ideal climate for floriculture and an enormous assortment of flora and fauna. J&K has Asia’s largest tulip garden.
J&K’s handicrafts are world famous, and the traditional handicraft industry has emerged as a large industry. Due to its large employment base and export potential, the industry has been receiving priority attention of the government. The UT is also famous for its small-scale and cottage industries such as carpet weaving, silks, shawls, basketry, pottery, copper and silverware, papier-mâché, and walnut wood. The cottage handicrafts industry provides direct and gainful employment to around 340,000 artisans.
As of March 2025, J&K had a total installed power-generation capacity of 3,607.09 MW, comprising 1,884.08 MW under central utilities, 1,576.47 MW (state/UT utilities) and 146.54 MW (private utilities). Of the total installed power-generation capacity until March 2025, 2,339.88 MW was contributed by hydropower, 881.22 MW (thermal power), 318.01 MW (renewable power) and 67.98 MW (nuclear power).
Total exports from J&K stood at Rs. 1,722 crore (US$ 200.94 million) in FY25 (until February).
Major items exported from J&K are drug formulations and biologicals, RMG wool, and manmade yarn fabrics.
The significant increase in tourist arrivals in J&K over the last two years was noted. In CY23, a total of 2.1 crore tourist visits were recorded in J&K, and this number rose to 2.3 crore in CY24, as was communicated to the House. This surge in tourism in the UT was fuelled by remarkable growth following the removal of Article 370.
The following are some of the major initiatives taken by the Government to promote Jammu & Kashmir as an investment destination:
- The government has placed a strong emphasis on highway development, particularly in regions such as Jammu and Kashmir, the northeastern states, and the hilly areas of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand. Currently, road construction projects valued at Rs. 2,00,000 crore (US$ 23.31 billion) are in progress in Jammu and Kashmir, which includes the construction of 105 tunnels. Additionally, the government is undertaking the construction of the Zojila tunnel, recognized as Asia's longest tunnel designed for sub-zero temperatures, with an estimated investment of around Rs. 6,000 crore (US$ 699 million).
- In June 2025, the Centre approved a Rs. 4,224 crore (US$ 488.49 million) PMGSY-IV package for 316 rural road projects covering 1,781 km in Jammu and Kashmir.
- In June 2025, the Centre approved 19 road and tunnel projects worth Rs. 10,637 crore (US$ 1.23 billion) to boost connectivity in the UT.
- In March 2025, Jammu & Kashmir Assembly approved Rs. 9,497 crore (US$ 1.1 billion) in grants for agriculture and allied sectors, including horticulture, animal husbandry, fisheries, agriculture, and rural development.
- In March 2025, the Government invested Rs. 29,903 crore (US$ 3.46 billion) to develop 1,003 km of national highways in J&K.
- Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi inaugurated, dedicated, and laid the foundation for numerous development projects worth over Rs. 46,000 crore (US$ 5.32 billion) in Jammu, spanning sectors like connectivity, aviation, healthcare, infrastructure, and petroleum.
- According to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India, J&K had 12.18 million wireless and tele-density of 90.13%, as of March 2025.
- Between FY20 and FY25, over Rs. 5,400 crore (US$ 624.49 million) worth of road and infrastructure projects have been implemented or proposed across Jammu and Kashmir under NABARD and RIDF schemes.
- Union Minister for Road Transport & Highways, Mr. Nitin Gadkari allocated of Rs. 1404.94 crore (US$ 169 million) for the Widening and Strengthening project of the Rafiabad – Kupwara – Chowkibal – Tangdhar – Chamkot section of National Highway-701.
- According to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), cumulative FDI inflow in J&K was valued at Rs. 11 crore (US$ 1.33 million) between October 2019-December 2024.
- Under the State/UT Budget 2023-24, Rs. 2,928.04 crore (US$ 357.4 million) has been allocated for housing and urban development.
- Raw silk production stood at 98 MT in FY 2021-22 in Jammu & Kashmir
- The Kashmir region is known for its horticulture industry. The industry plays a vital role in the UT’s economic development. In 2023-24, the total production of vegetables and fruits in the UT was estimated at 1,996.18 thousand metric tonnes and 2,643.24 thousand metric tonnes, respectively.
- J&K has an industrial policy that offers attractive incentives along with a single-window clearance mechanism. Land is allotted at concessional rates in industrial areas on lease for 90 years.
- National Highway Infrastructure Development Corporation (NHIDCL) is developing five tunnels in the UT at a cost of US$ 3.42 million. The tunnels will have all weather access and will be completed by 2024.
- In FY23, 543 new projects with a total cost of Rs. 2,237 crore (US$ 292.2 million) will be sanctioned with NABARD funding.
- An elevated light metro rail system is expected to be rolled out in 2022-23 and is likely to be completed in 2026. This will reduce the traffic congestion in Srinagar & Jammu.
Note: P - Provisional, T - Target, MT - Million Tonnes, * Including Ladakh Union Territory




